Currency Indices
Can Everyday Commodities/Products Predict Foreign Exchange Rates?
It seems that everyday products can provide a good indicator regarding foreign exchange rates. Forex analysts use standard global products or services to determine the ‘fair value’ of an exchange rate.
In addition, standardized products, such as coffee, can be used for developing interesting Indexes. Some of these indexes include the MacDonald’s Big Mac Index and the Starbucks Latte Index. There is also the “Domino’s Medium Pepperoni Pizza Index” and the “Nobu Black Cod with Miso Index”.
Creating Indexes by Using Standard Products
- Starbucks Latte Index
- MacDonald’s Big Mac Index
- Domino’s Medium Pepperoni Pizza Index
- Nobu Black Cod with Miso Index
The Wall Street Journal “Latte Index”
In 2013, the Wall Street Journal created the "Latte Index" which tracks the price of a Starbucks Grande Latte in major cities. The price of a Grande Latte is compared in 29 different countries:
(i) All prices are converted to US Dollars, and
(ii) they are compared to the Starbucks Latte price in New York City, which works as a benchmark price. The price of Starbucks Latte in New York is US$3.45.
How Does The Starbucks Latte Index Work?
The “Latte Index”, uses PPP (Purchasing-Power Parity) to compare the cost of the same commodity (Latte Coffee) in different countries –in order to determine overvalued and undervalued currencies. The Index can measure how many coffee cups can purchase a minimum-wage earner with its hourly pay. In countries with a strong currency, it would take more dollars to buy a Starbucks latte than in countries with a currency that has less buying power.
The report of WSJ included twenty-nine (29) cities, and the benchmark was New York, where the Starbucks latte cost $3.45. Actually, New York ranked in the middle of the list (14th place).
The WSJ wrote: “Though the latte prices are likely also affected by factors such as country taxes, The Wall Street Journal’s Latte Index broadly mirrors the results of other valuation methods.”

Example
For example, the USD price of a latte in Zurich, Switzerland is $5.76, while the USD USD price of a latte in Mexico City, Mexico is $2.19. According to the “Latte Index”, the Swiss Franc is 66% overvalued against the US Dollar while the Mexican Peso is 36% undervalued against the US Dollar. If we consider, that the Swiss Franc is a ‘hard currency’ focused on monetary-stability, and the Mexican Peso is a ‘flexible currency’ focused towards easy-exports, then the findings may reflect somehow the truth.
MORE ON CARRYTRADER
| ■ COMPARE PROVIDERS | ► Brokers for Carry Traders | ||||||
| ■ CURRENCY PAIRS | ► EURUSD | ► GBPUSD | ► USDJPY | ► EURGBP | ► AUDUSD | ► NZDUSD | ► USDCAD |
| ■ GLOBAL MARKETS | » Gold |
|
|
||||
| ■ LEARNING RESOURCES | » Currency indices | » CBOE Indices | » Forex Fundamentals | » The History of Interest Rates |
■ The Starbucks Latte Index
CarryTrader.com

US Dollar Index (USD INDEX -USDX)
The US Dollar Index or USDX is a currency index that describes the value of the US dollar against a basket of major Forex currencies.
The US Dollar Index
USDX can measure the overall strength of the US Dollar against the strength of other major Forex Currencies. In addition, Forex traders can assess technical analysis on the historic chart of the USDX Index by drawing support and resistance, trendlines etc.
Six (6) Forex Currencies and their Weight
The USDX uses a weighted mean system for measuring the USD value against a basket of six major Forex:
Table: Six Forex Currencies and their Weight on USDX
|
FOREX CURRENCY |
SYMBOL |
WEIGHT (%) |
|
European Euro |
EUR |
57.60% |
|
Japanese Yen |
JPY |
13.60% |
|
British Pound Sterling |
GBP |
11.90% |
|
Canadian Dollar |
CAD |
9.10% |
|
Swedish Krona |
SEK |
4.20% |
|
Swiss Franc |
CHF |
3.60% |
|
Total |
100% |
|
Note: This basket of currencies does not include some major trading partners of the US such is China, Brazil, and Korea.
The Big Mac index
The Big Mac Index is a currency index implementing the Purchasing-Power Parity theory (PPP). The Index was originally created in 1986 by ‘The Economist’.
What is the Big Mac Index?
The Big Mac index is a currency index that uses the famous Big-Mac Menu to show if the global currencies are trading at their ‘fair levels’. This funny but economically-logical approach is called as the ‘Burgernomics’ and has been the subject of tens of Academic Studies around the world.
Big Mac index and the PPP Theory
Actually, the Big Mac index is an implementation of the Purchasing-Power Parity theory (PPP). According to the PPP theory, the long run currency rates should fluctuate in a manner that equalizes the price of identical goods and services. In the case of the Big Mac index, the price used is the price of the Big Mac burger.
An Example using the Big Mac index
Let’s say that the price of the Big Mac burger during summer averaged $5.00 in the US and $2.50 in Indonesia. According to the Big Mac index, the Indonesian currency is undervalued by 50%.
Here is the link to the official Big-Mac Index: ► http://www.economist.com/content/big-mac-index
 Major Euro Currency Indices
Major Euro Currency Indices
There are quite a few Euro Currency Indices aiming to measure the value of Euro against a basket of other major currency rates.
These are the most important Euro Currency Indices:
- Euro Currency Index (EUR_I)
- Euro Effective Exchange Rate Index (EER-20)
- Dow Jones Euro Indices (former)
- New York Board of Trade -ECX, EURX, EXY (former)
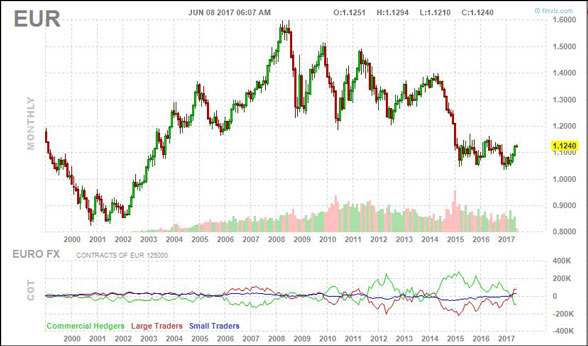
Chart: The EURO Index
Source: FinViz Currency Indices
(1) Euro Currency Index (EUR_I)
The Euro Currency Index is an index that reflects the exchange rate of four (4) currencies against the Euro. These four currencies are:
1. US-Dollar
2. British Pound Sterling
3. Japanese Yen
4. Swiss Franc
The Euro Currency Index was launched in 2004 and the base is 100 points commencing on January, 4th 1971. As the Euro currency was launched in 1999 before that year the Euro Currency Index is calculated based on the Deutsche Mark.
Table: Weighting of the 4 currencies against the euro
|
Currency |
Code |
Weight |
|
US Dollar |
USD |
25% |
|
British Pound Sterling |
GBP |
25% |
|
Japanese Yen |
JPY |
25% |
|
Swiss Franc |
CHF |
25% |
|
Total |
100% |
|
» The Euro Index (EUR_I) at Stooq